How to Read Tire Date Code
When and where was your car tire manufactured? Tires bought from a retailer are not necessarily new. Old tires tend to escalate safety risks and increase car repair costs. Luckily, car owners can easily identify and track the age and origin of their tires using DOT code.
What is Tire Date Code?
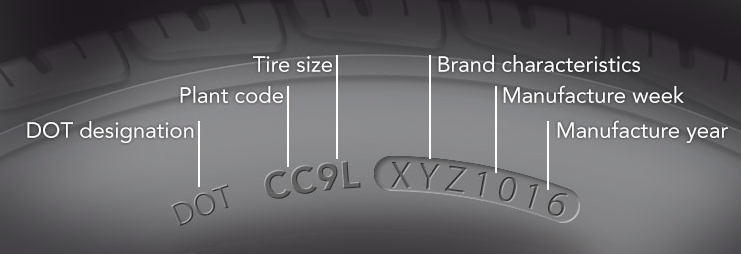
Tires having this code have met the minimum safety compliance standards as stipulated by the US Department of Transport. Tire date code provides information on the exact location that the tire was manufactured, manufacturer’s code, week, and year of manufacture.
Standard tire date codes begin with DOT, followed by 8 to 13 alphanumeric characters, e.g. DOT DA JM9E 0519. 0519 implies that the tire was manufactured in the fifth week of 2019.
Where to Find DOT Code on the Tire
There are no strict regulations on where manufacturers should position the tire date code. However, most tire manufacturers inscribe the date codes on the sidewalls of the tire, usually near the edge of the rim.

Manufactured during the 51st week of the 2017 year
Why Should I Be Concerned About the Tire Date Code?
Purchasing tires from retailers does not necessarily guarantee that those are new tires. In reality, it takes time for new tires to reach retailers. The tires could also lie in storage for several months or years before purchase.
Confirming the date code on tires provides a clue of how long the tires have taken under storage. Tires stored under poor conditions are prone to damage and premature aging, which may negatively impact car handling properties.
How Old Are Your Tires? (How Old is Too Old?)
The Department of Transportation advises car owners to replace their tires after every ten years. On the other hand, associations in the tire industry agree that the useful life of a rubber tire is between six and ten years.
Tires wear and tear at different rates. Differences in storage conditions, maintenance procedures and usage makes it difficult to predict the service life of a tire based on its DOT calendar age.
Tires that appear older at the time of purchase can still perform well if given proper care and maintenance over its service life. It is recommended that tires should be inspected and replaced after every 7 years.
How to Properly Store Tires for Increased Life
Rubber weakens when exposed to extreme weather conditions. Proper storage, care, and maintenance extend the service life of tires. Tire damage is evidenced by the presence of shallow cracks on sidewalls or whitening of rubber.
- When transporting and storing tires, it is advisable that they are contained in cool and dry conditions, preventing exposure to humidity and ultraviolet rays.
- Tires should be stored on raised platforms off the ground, in a vertical orientation. Stacking tires horizontally on top of each other increases the possibility of distortion and physical damage of tires.
- Clean tires with soap and water, getting rid of all dirt and ensuring they’re completely dry before storing used tires.
Common Misconceptions About DOT Code Tire Age
- Most people are advised to purchase tires whose DOT code lies within the same year. Often, tires take several months to be shipped from the manufacturers to the target markets. Tires with older DOT codes will work perfectly well as long as they were stored and transported in recommended conditions.
- There are assumptions that the DOT code represents the dates when the tires were first approved for legal use by the Department of Transport. It only represents the actual dates that the tires were manufactured.
FAQ
How do I know when my tires expire?
It is almost impossible to pinpoint the service life of any tire based on the tire date code. It is recommended that car owners inspect and probably replace their tires every 7 years. Service life varies depending on how well you handle and maintain your car tires.
How long do tires last if not used?
Tires last between 6 and 10 years if left unused.The time varies depending on storage and environmental conditions.
Do tires get hard with age?
All rubber tires lose their elastic properties over years. Continuous decrease in elasticity causes hardening of tires and occurs irrespective of tire usage conditions.





